HD 181327: Astronomers Detect Water Ice In Its Circumstellar Disk
Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit NewsOneSMADCSTDO now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
Astronomers Detect Water Ice in the Circumstellar Disk of HD 181327: A Giant Leap for Planet Formation Understanding
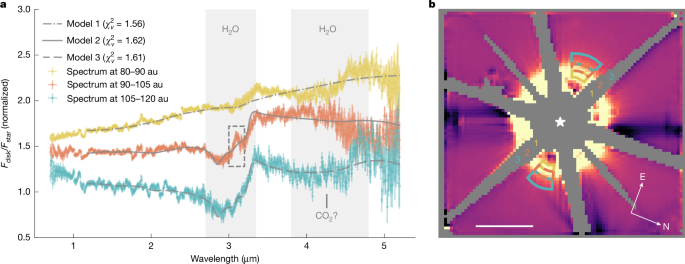
A team of astronomers has made a groundbreaking discovery, detecting significant amounts of water ice within the circumstellar disk surrounding the young star HD 181327. This exciting find offers crucial insights into the formation of planets and the potential for habitable worlds around other stars. The research, published in [Insert Journal Name and Publication Date here], utilizes data from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) to paint a detailed picture of this fascinating stellar system.
HD 181327: A Star System of Interest
HD 181327, located approximately 163 light-years away in the constellation of Sagittarius, is a relatively young star roughly twice the mass of our Sun. It's already known for its prominent circumstellar disk – a swirling cloud of gas and dust from which planets can form. However, the detection of water ice adds a vital new layer to our understanding of this system and the processes governing planet formation.
The Significance of Water Ice Detection
The presence of substantial water ice in the HD 181327 disk is incredibly significant for several reasons:
- Planet Formation: Water ice acts as a crucial building block for planets. It's incorporated into planetesimals – the precursors to planets – and plays a vital role in the accretion process. The abundance of water ice detected suggests a high potential for planet formation within this system.
- Habitable Worlds: The presence of water, even in the form of ice, is a key ingredient for the potential development of habitable environments. While the ice is currently far from the star, future migration of icy planetesimals could deliver water to regions more conducive to liquid water and potentially life.
- ALMA's Power: This discovery highlights the incredible capabilities of the ALMA telescope. Its high sensitivity and resolution allow astronomers to detect and analyze subtle features in distant star systems, revealing details previously hidden from view.
Details of the Discovery
The ALMA observations revealed a surprisingly large amount of water ice concentrated in the outer regions of the HD 181327 disk. This ice is likely mixed with dust and other molecules, forming a complex and dynamic environment. The team used advanced spectroscopic techniques to identify the unique signature of water ice within the disk's emission. This detailed analysis provides crucial information about the composition and temperature of the disk.
Future Research and Implications
This discovery opens up numerous avenues for future research. Astronomers will continue to monitor HD 181327 to learn more about its disk's evolution, the potential for planet formation, and the likelihood of finding exoplanets within this system. The findings also contribute to a broader understanding of how water, a vital component for life as we know it, is distributed throughout the universe and incorporated into planetary systems. Further observations using ALMA and other powerful telescopes will undoubtedly yield even more exciting discoveries in the years to come, furthering our understanding of the universe and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Keywords: HD 181327, water ice, circumstellar disk, planet formation, exoplanets, ALMA, Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array, habitable worlds, star formation, astronomy, space, exoplanet research.

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on HD 181327: Astronomers Detect Water Ice In Its Circumstellar Disk. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
 Google And C Span Understanding The Networks Ongoing Dispute
May 16, 2025
Google And C Span Understanding The Networks Ongoing Dispute
May 16, 2025 -
 Report Of Criminal Probe Sends United Health Shares Down
May 16, 2025
Report Of Criminal Probe Sends United Health Shares Down
May 16, 2025 -
 Inspirational Quote Paolini Reflects On Schiavones Influence On Tennis
May 16, 2025
Inspirational Quote Paolini Reflects On Schiavones Influence On Tennis
May 16, 2025 -
 Cma Fest Fan Fair X Lineup So Fis Star Studded Showcase Announced
May 16, 2025
Cma Fest Fan Fair X Lineup So Fis Star Studded Showcase Announced
May 16, 2025 -
 Quantum Computing Companys Profit Surge Drives Stock Price Higher
May 16, 2025
Quantum Computing Companys Profit Surge Drives Stock Price Higher
May 16, 2025
