In-Situ Resource Utilization: Project Orion's Martian Uranium Propulsion System
Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit NewsOneSMADCSTDO now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
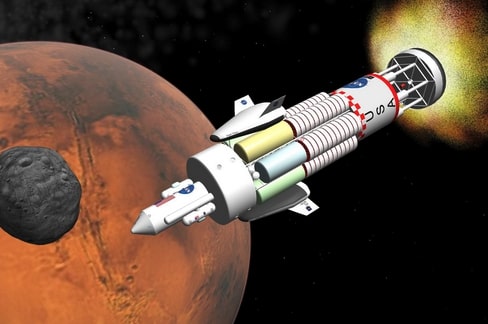
In-Situ Resource Utilization: Project Orion's Martian Uranium Propulsion System – A Giant Leap for Space Exploration
Harnessing the Red Planet's Riches: A Revolutionary Approach to Deep Space Travel
The quest for interstellar travel has long been hampered by the limitations of carrying massive amounts of propellant. Project Orion, a now-declassified Cold War-era concept, offered a radical solution: nuclear pulse propulsion. While the project itself never launched, its underlying principles – particularly the utilization of in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) – remain incredibly relevant to future space exploration, especially concerning missions to Mars. This article delves into the potential of using Martian uranium for a modified Orion propulsion system, a prospect that could revolutionize deep-space travel and significantly reduce mission costs.
Project Orion: A Nuclear Vision
Project Orion envisioned spacecraft propelled by a series of controlled nuclear explosions. While the sheer scale and potential dangers were significant, the project's potential for reaching distant destinations at unprecedented speeds was undeniable. The key? Utilizing massive amounts of propellant – a significant hurdle for any long-duration space mission. But what if that propellant could be sourced on the destination planet?
Martian Uranium: Fueling the Future
Mars possesses significant reserves of uranium, a potent nuclear fuel source. Mining and refining this uranium on Mars, through ISRU techniques, presents a compelling alternative to launching all necessary fuel from Earth. This drastically reduces the initial launch mass, translating to significant cost savings and enhanced mission feasibility.
Adapting Project Orion for Martian ISRU:
A modern, Martian-adapted Orion system would require several key innovations:
- Autonomous Mining and Refining: Robotic systems would be crucial for extracting and processing Martian uranium ore, minimizing the need for human intervention in this hazardous environment. This requires advancements in robotics, materials science, and nuclear engineering.
- Miniaturized Nuclear Explosions: Smaller, more controlled nuclear explosions would be necessary for a safer and more efficient propulsion system, potentially leveraging modern advancements in nuclear fusion technology.
- Radiation Shielding: Protecting astronauts from the radiation generated by repeated nuclear pulses would be paramount, demanding the development of advanced shielding materials and strategies.
- Sustainable Energy Sources: Powering the mining, refining, and propulsion systems would require a combination of solar, nuclear, and potentially even geothermal energy sources on Mars.
The Benefits of Martian Uranium Propulsion:
The advantages of using Martian uranium for a modified Orion system are substantial:
- Reduced Launch Mass: Significantly lowers the cost and complexity of launching the spacecraft from Earth.
- Increased Payload Capacity: Allows for larger payloads, including more scientific equipment, habitats, and life support systems.
- Faster Travel Times: Enables faster travel times to Mars and beyond, significantly shortening mission durations.
- Enhanced Mission Sustainability: Reduces reliance on Earth-based resources, paving the way for longer, more independent missions.
Challenges and Future Research:
Despite its potential, several challenges remain:
- Technological Development: Significant technological advancements are needed in robotics, nuclear engineering, and materials science.
- Environmental Impact: The environmental consequences of nuclear explosions on Mars require careful assessment and mitigation strategies.
- International Cooperation: Developing and deploying such a system would require significant international collaboration and regulatory frameworks.
Conclusion:
Utilizing Martian uranium for a modified Orion propulsion system represents a bold yet potentially transformative approach to deep-space exploration. While significant challenges remain, the potential benefits – reduced launch costs, increased payload capacity, and faster travel times – make it a compelling area of future research. This concept highlights the crucial role of ISRU in enabling sustainable and cost-effective exploration of our solar system and beyond. The legacy of Project Orion, albeit adapted for the Martian environment, could well propel humanity towards a new era of spacefaring.

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on In-Situ Resource Utilization: Project Orion's Martian Uranium Propulsion System. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
 The Bachelor Tv Schedule Tonights Episode And Future Finale Dates
Mar 18, 2025
The Bachelor Tv Schedule Tonights Episode And Future Finale Dates
Mar 18, 2025 -
 Atul Gawande Responds To Elon Musks Assault On Usaid A Looming Catastrophe
Mar 18, 2025
Atul Gawande Responds To Elon Musks Assault On Usaid A Looming Catastrophe
Mar 18, 2025 -
 Snow Whites Modern Adaptation A Deep Dive Into The Surrounding Controversy
Mar 18, 2025
Snow Whites Modern Adaptation A Deep Dive Into The Surrounding Controversy
Mar 18, 2025 -
 Golden State Warriors Aim To Defeat Nikola Jokic And The Denver Nuggets
Mar 18, 2025
Golden State Warriors Aim To Defeat Nikola Jokic And The Denver Nuggets
Mar 18, 2025 -
 Korban Banjir Blora Pria Tewas Terseret Arus Saat Shalat
Mar 18, 2025
Korban Banjir Blora Pria Tewas Terseret Arus Saat Shalat
Mar 18, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Myles Lewis Skelly Arsenal Fans Reaction To His Goal Vs Man City A Shock
Apr 30, 2025
Myles Lewis Skelly Arsenal Fans Reaction To His Goal Vs Man City A Shock
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Patient Privacy At Risk Thousands Of Health Records Potentially Compromised
Apr 30, 2025
Patient Privacy At Risk Thousands Of Health Records Potentially Compromised
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Cardano Ada Price Crucial Support Level Tested 1 Breakout Possible
Apr 30, 2025
Cardano Ada Price Crucial Support Level Tested 1 Breakout Possible
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Live Review Hans Zimmer Delivers In Sydney
Apr 30, 2025
Live Review Hans Zimmer Delivers In Sydney
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Delhi Capitals Suffer Third Home Defeat Kkrs Narine Steals The Show
Apr 30, 2025
Delhi Capitals Suffer Third Home Defeat Kkrs Narine Steals The Show
Apr 30, 2025
