Understanding The Viral-Dementia Connection: What Scientists Are Discovering
Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit NewsOneSMADCSTDO now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
Understanding the Viral-Dementia Connection: What Scientists are Discovering
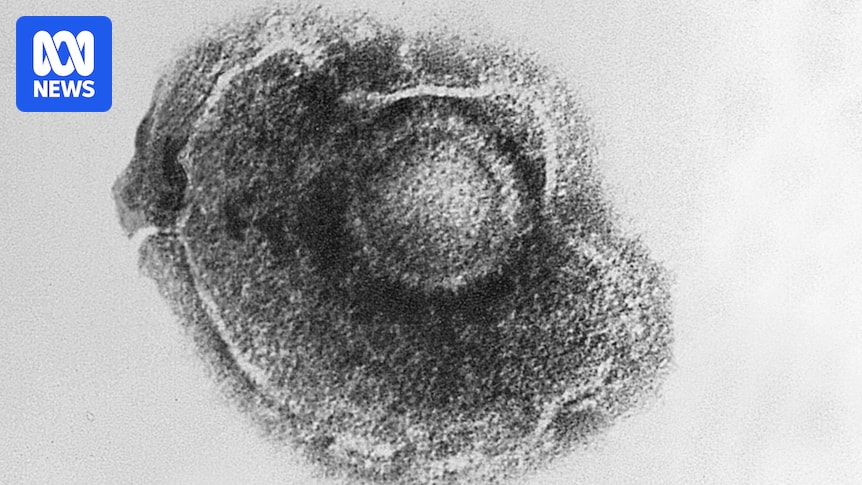
Dementia, a debilitating condition affecting millions worldwide, is increasingly being investigated for potential links to viral infections. While Alzheimer's disease remains the most common cause, research is uncovering a complex relationship between viruses and the development or progression of various dementia types. This article explores the latest scientific discoveries shedding light on this crucial connection.
The Growing Evidence: Viruses as Dementia Risk Factors
For years, researchers have suspected a correlation between viral infections and neurodegenerative diseases like dementia. Recent studies are strengthening this hypothesis, pointing to several potential mechanisms:
-
Direct neuronal damage: Some viruses, such as herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1), can directly infect and damage brain cells, contributing to cognitive decline and dementia symptoms. Studies have shown a link between HSV-1 reactivation and increased Alzheimer's disease risk.
-
Inflammation and immune response: Viral infections trigger inflammatory responses within the brain. Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of many neurodegenerative diseases, potentially accelerating the damage and progression of dementia. This inflammatory process can disrupt neuronal function and contribute to cognitive impairment.
-
Amyloid-beta plaque formation: Research suggests that viral infections may influence the production and accumulation of amyloid-beta plaques, a characteristic feature of Alzheimer's disease. These plaques are believed to play a significant role in the disruption of neuronal communication and cognitive decline.
-
Tau protein tangles: Similar to amyloid-beta plaques, viral infections might also contribute to the formation of tau protein tangles, another hallmark of several dementias, including Alzheimer's disease. The exact mechanisms remain under investigation, but accumulating evidence suggests a potential link.
Specific Viruses Under Scrutiny
Several viruses are currently under intense scrutiny for their potential role in dementia:
-
Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1): This common virus is strongly implicated in a range of neurological disorders, and its reactivation in the brain is being investigated as a potential risk factor for Alzheimer's disease and other dementias.
-
Cytomegalovirus (CMV): A widespread herpesvirus, CMV infection is linked to increased inflammation in the brain and has been associated with accelerated cognitive decline in individuals with pre-existing dementia.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): HIV infection is known to cause HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND), a form of dementia. Research continues to explore the complex interplay between HIV and brain function.
Challenges and Future Research Directions
While the evidence is mounting, several challenges remain in fully understanding the viral-dementia connection:
-
Complex interplay of factors: Dementia is a multifaceted condition, and viral infections are likely only one piece of a complex puzzle. Genetic predisposition, lifestyle factors, and other environmental exposures also contribute to the risk.
-
Longitudinal studies: Long-term studies are needed to definitively establish causal relationships between specific viral infections and dementia development. Observational studies can only show correlation, not causation.
-
Developing preventative strategies: If a strong causal link is established, developing effective preventative strategies, such as antiviral therapies or vaccines, could be crucial in mitigating the risk of dementia.
Conclusion: A Promising Area of Investigation
The emerging research linking viral infections to dementia represents a significant breakthrough in our understanding of this devastating condition. While more research is needed to establish definitive causal links and develop effective interventions, the current findings highlight the importance of continued investigation into the role of viruses in the pathogenesis of dementia. This could pave the way for novel therapeutic strategies and preventive measures, ultimately improving the lives of millions affected by this debilitating disease.

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on Understanding The Viral-Dementia Connection: What Scientists Are Discovering. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
 Unravel Nyt Connections Hints And Answers For April 20th Game 679
Apr 22, 2025
Unravel Nyt Connections Hints And Answers For April 20th Game 679
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Giants Stars Downfall Crows Seize Opportunity For Key Victory
Apr 22, 2025
Giants Stars Downfall Crows Seize Opportunity For Key Victory
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Timberwolves Dominate Game 1 Redick Highlights Lakers Internal Problems
Apr 22, 2025
Timberwolves Dominate Game 1 Redick Highlights Lakers Internal Problems
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Nhl Playoffs Avalanche And Stars Tied After Blackwells Overtime Winner
Apr 22, 2025
Nhl Playoffs Avalanche And Stars Tied After Blackwells Overtime Winner
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Improved Volume Control Coming To You Tube Music
Apr 22, 2025
Improved Volume Control Coming To You Tube Music
Apr 22, 2025
